In today’s world, harnessing solar power is not only a trend but a necessity. With solar power systems becoming more prevalent, understanding the components that make these systems efficient is crucial. Among these components, solar charge controllers play a vital role in managing the flow of electricity from solar panels to batteries. If you’re a solar enthusiast, eco-conscious consumer, or just starting to explore solar systems, you’ll find that choosing the right solar charge controller can significantly impact your solar power efficiency.
In this guide, we’ll explore the difference between MPPT and PWM solar charge controllers and help you decide which one suits your needs best.
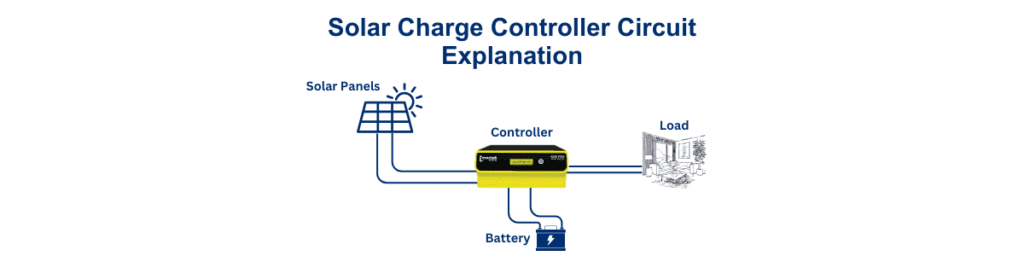
Understanding Solar Charge Controllers
Solar charge controllers are essential in solar power systems. They regulate the flow of electricity from solar panels to batteries, ensuring that batteries are not overcharged. This prolongs battery life and maintains system efficiency. Without a charge controller, solar panel energy could damage your batteries, leading to costly repairs or replacements.
Two main types of solar charge controllers exist:
Both serve the same purpose, but they do so in different ways, impacting overall system performance.
What is PWM Charge Controller?
A PWM charge controller is a straightforward technology that connects the solar array directly to the battery bank. Its primary function is to taper the charging current as the battery nears full charge. Here’s how it works:
- Direct Connection: The PWM controller connects the solar panels directly to the battery.
- Voltage Regulation: It reduces the voltage of the solar array to match the battery voltage.
- Efficiency: It operates at lower efficiency, typically around 70-80%.
Benefits of PWM Controllers:
- Cost: PWM controllers are generally more affordable than MPPT controllers
- Simplicity: Their straightforward design makes them easy to install and use.
- Durability: Fewer components mean fewer parts that can fail.
Drawbacks of PWM Controllers:
- Lower Efficiency: They don’t adjust to changing environmental conditions well.
- Limited Flexibility: They require solar panel voltage to closely match the battery voltage.
Typical Use Cases for PWM Controllers:
- Small Systems: Ideal for smaller solar systems where cost is a concern.
- Constant Conditions: Best used in environments with stable temperatures and consistent sunlight.
What is MPPT Solar Charge Controller?
The MPPT solar charge controller full form, short for Maximum Power Point Tracking, is more advanced. It optimizes the power output from solar panels by adjusting the electrical operating point of the modules. Here’s how MPPT technology works:
- Power Optimization: MPPT controllers track the optimal power point of the solar panels.
- Voltage Adjustment: They convert higher voltage from panels to lower voltage to efficiently charge batteries.
- Efficiency: Typically operate at 95%+ efficiency, extracting maximum energy from solar panels.
Benefits of MPPT Controllers:
- Higher Efficiency: They can harness up to 30% more energy compared to PWM controllers.
- Versatility: Perform well in varying weather conditions, maximizing energy extraction.
- Adaptability: Can work with different solar panel and battery voltages.
Drawbacks of MPPT Controllers:
- Cost: Generally more expensive than PWM controllers.
- Complexity: More components mean they can be more complex to install and maintain.
The Use of MPPT:
- Changing Conditions: Perfect for areas with fluctuating weather patterns.
- Larger Systems: Ideal for larger solar installations where efficiency gains are crucial.
Difference Between PWM and MPPT
When comparing MPPT vs PWM, several factors come into play:
| Aspect | PWM | MPPT |
|---|---|---|
| Efficiency | 70-80% | 95%+ |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Complexity | Simple | Complex |
| Environmental Adaptability | Limited | High |
| Voltage Flexibility | Matches battery voltage | Adjusts to maximize power output |
| Ideal Use | Small, stable environments | Large, variable environments |
Technical Difference:
- Handling Power: MPPT adjusts input voltage for optimal power harvesting, whereas PWM directly connects panels to batteries.
- Performance: MPPT controllers outperform PWM in extracting energy, especially in diverse conditions.
Which Solar Charge Controller is Best for You?
Deciding between PWM and MPPT solar controller involves evaluating several factors:
1. System Size:
- Smaller systems can benefit from cost-effective PWM controllers.
- Larger systems need MPPT for maximum efficiency.
2. Environmental Conditions:
- Stable climates favor PWM, while variable climates benefit from MPPT.
3. Budget Considerations:
- PWM controllers are budget-friendly, but MPPT offers better long-term savings.
4. Voltage Requirements:
- If panel and battery voltages don’t match, MPPT is the way to go.
When to Choose PWM:
- If you have a small solar setup with a tight budget and stable environmental conditions.
When to Choose MPPT:
- If your system is larger, you have variable weather, or mismatched panel and battery voltages.
Conclusion
In the world of solar power, understanding the difference between MPPT and PWM solar charge controllers is vital for optimizing your system. Both have their strengths and weaknesses, and the right choice depends on your specific needs.
For solar enthusiasts and eco-conscious consumers, selecting the appropriate controller will not only enhance efficiency but also ensure the longevity of your solar power system. Remember, investing in the right technology today will pave the way for a greener tomorrow.
Explore more about solar technologies and take the next step in your renewable energy journey.


